How to fix ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR: causes, variations, and troubleshooting

ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR is a common issue users face when a website fails to establish a secure connection. This error typically arises due to problems with SSL/TLS certificates or misconfigurations, preventing users from accessing sites securely.
Encountering ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR can be frustrating because it disrupts the browsing experience and raises concerns about data security and privacy.
This article will explain what ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR is, why it happens, and how it looks across different browsers. We’ll also provide step-by-step solutions to fix this website security error effectively.
What is ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR?
In essence, ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR indicates an issue in the SSL/TLS handshake process, an essential step in the authentication process between the client (browser) and the server.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) are cryptographic protocols that secure data transmitted over the internet. When the SSL/TLS handshake fails, the browser can’t verify the server’s identity, resulting in a broken connection.
As a result, modern browsers like Google Chrome or Safari automatically block any connection that isn’t secure to protect users from potential threats. This prevents visitors from accessing the intended website.
Common causes of ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR
ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR can occur due to several SSL/TLS protocol-related issues, such as:
- Misconfigured SSL certificates. If the SSL certificate is improperly installed, expired, or doesn’t match the domain name, the browser cannot establish a secure connection to the server.
- Incorrect date and time settings. SSL/TLS certificates have a specific validity period. If the device’s date and time settings are incorrect, the browser may perceive the certificate as expired or invalid.
- Outdated browser or operating system. Browsers and operating systems that aren’t up to date may lack support for the latest protocols or security standards, leading to SSL errors.
- Mixed content issues. If a website loads secure (HTTPS) and non-secure (HTTP) content, it can cause an SSL/TLS handshake failure.
- Firewall or antivirus interference. Some firewall or antivirus software scans SSL/TLS connections to protect against threats. This can sometimes lead to conflicts or blocked connections, triggering the error.
How does ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR look on different browsers?
ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR can present differently depending on the web browser you use. Here’s how this SSL certificate error appears across popular browsers:
Google Chrome
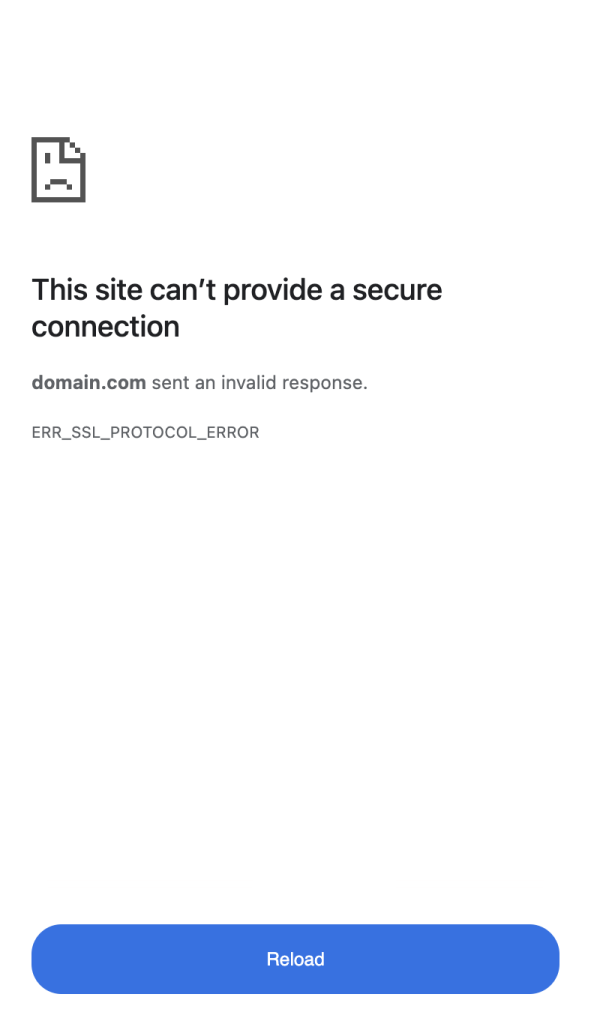
In Google Chrome, the error message shows as “This site can’t provide a secure connection” and “[website] sent an invalid response.” It’s followed by the ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR error code and a Reload button.

Microsoft Edge
Microsoft Edge displays the messages “The connection for this site is not secure” and “[website] sent an invalid response.”, the ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR code, and a Refresh button. It also provides a Diagnose issue option to help users troubleshoot the problem.
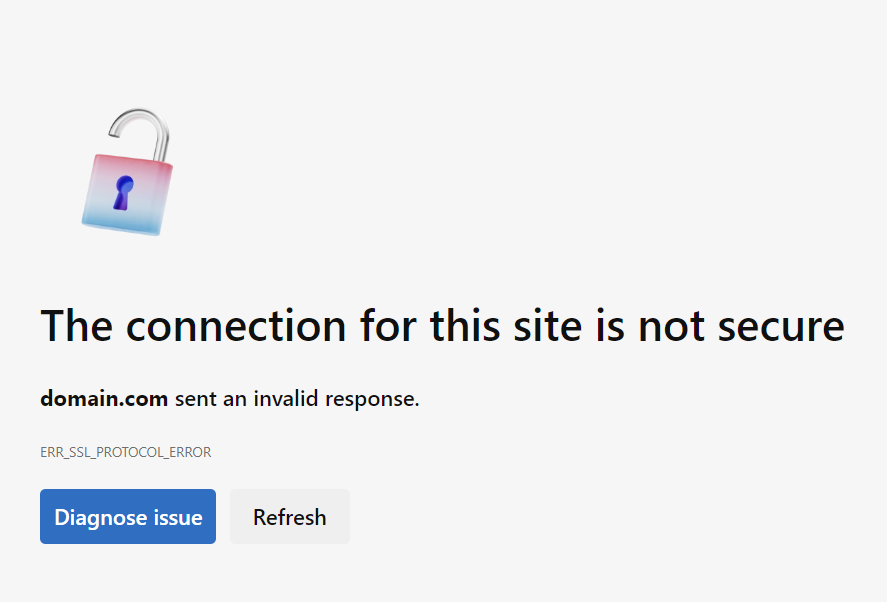
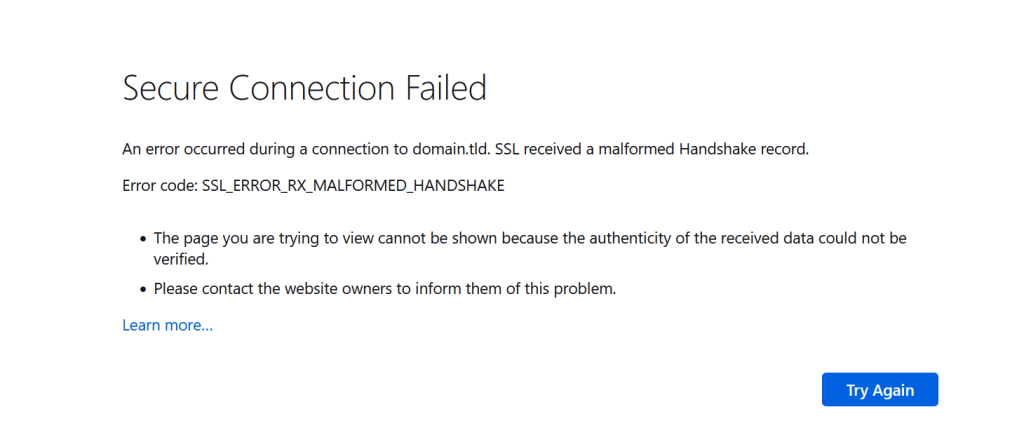
Mozilla Firefox
Firefox presents the “Secure Connection Failed” message and the SSL_ERROR_RX_MALFORMED_HANDSHAKE error code. Unlike Chrome and Edge, it provides possible causes for the error and suggested actions to resolve the issue.
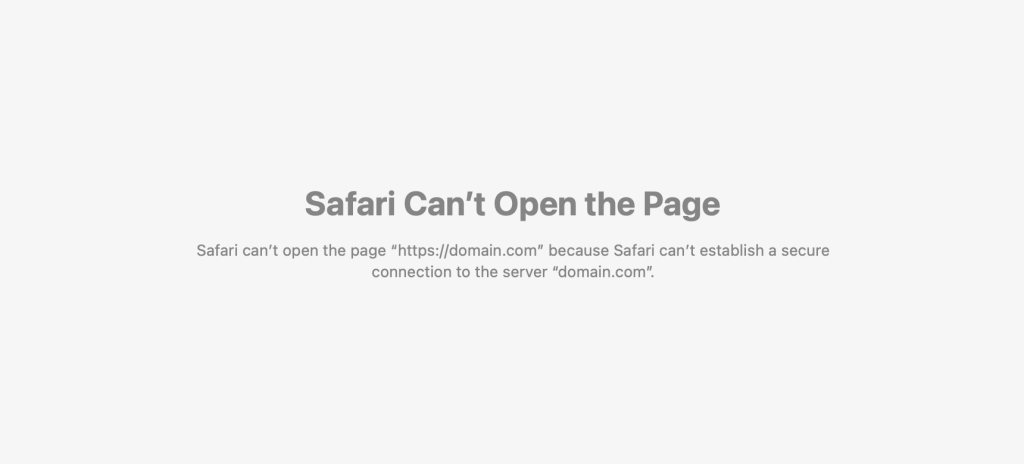
Safari
Safari displays the error “Safari Can’t Open the Page,” followed by “Safari can’t open the page [website] because Safari can’t establish a secure connection to the server [website].” Compared to other browsers, Safari doesn’t provide the actual error code or detailed information.
Mobile browsers
The error messages on mobile browsers like Chrome for Android and Safari for iOS are similar to their desktop counterparts but simplified for mobile screens. Chrome for Android displays the same “This site can’t provide a secure connection” message, while Safari for iOS shows “Safari Can’t Open the Page.”
How to fix ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR
Here are several methods to effectively fix ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR. We recommend starting with the basic steps and moving to more advanced solutions if the problem persists.
Check the date and time settings
Incorrect date and time settings on your device can cause SSL errors like ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR. As explained earlier, SSL/TLS certificates have specific validity periods, and a wrong system date and time can cause browsers to perceive the certificate as expired.
Here’s how to adjust the date and time settings on different operating systems. Please note that the steps may vary depending on the brand and OS version. Make sure to connect your device to the internet so the settings apply correctly.
Windows
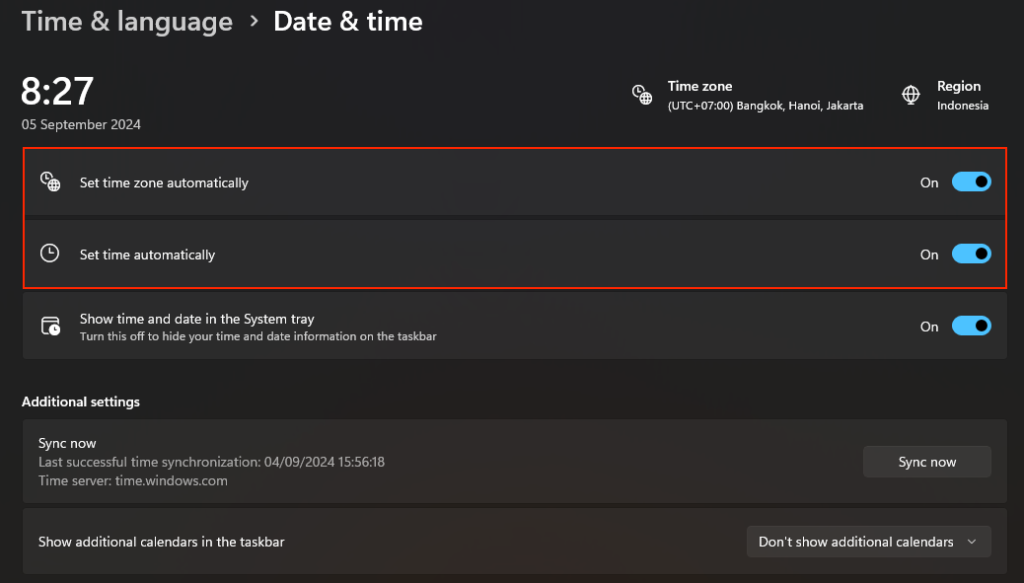
- Click the Start menu and select Settings.
- Go to Time & language → Date & time.
- Toggle Set time automatically and Set time zone automatically to On. If they’re already on, turn them off and back on.
macOS
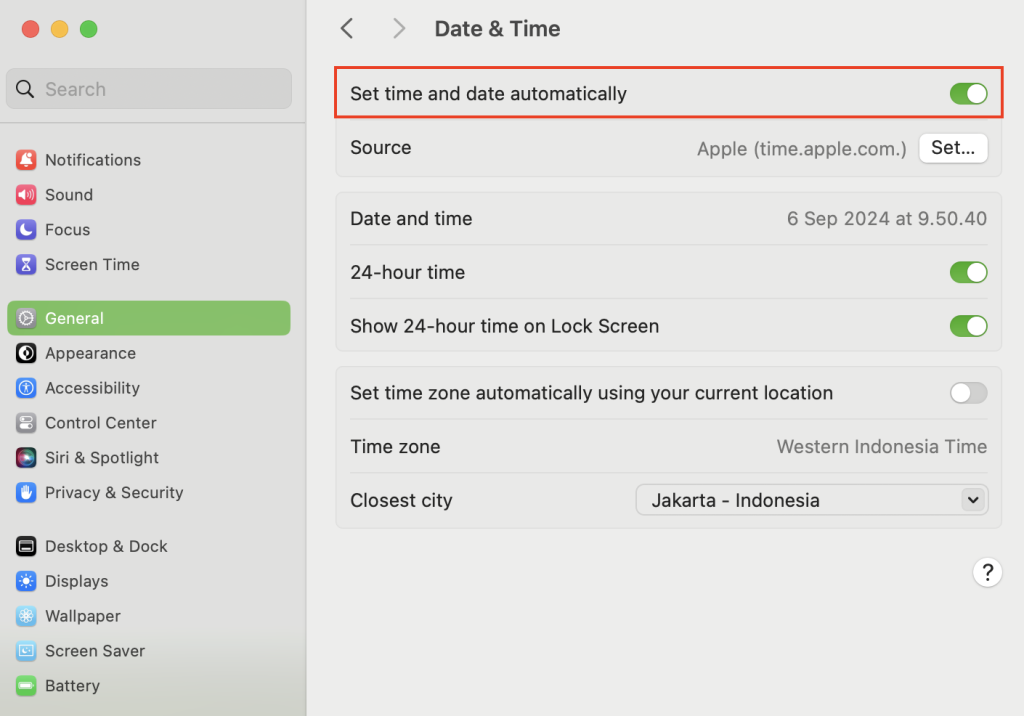
- Go to the Apple menu and select System Settings.
- Navigate to General → Date & Time.
- Activate the Set date and time automatically option.
Android
- Open the Settings menu.
- Tap General management → Date and time.
- Set Automatic date and time, Automatic time zone, and Set time zone based on location to On.
iOS
- Navigate to Settings → General → Date & Time.
- Enable Set Automatically.
Clear browser cache, cookies, and SSL state
Cached data and cookies stored in your browser can sometimes conflict with SSL certificates, leading to ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR. Old or corrupt data can also prevent the browser from verifying the certificate correctly.
Clearing your browser’s cache, cookies, and SSL state can resolve these conflicts and ensure a fresh handshake. Follow these steps:
Google Chrome
- Click the three vertical dots icon in the top-right corner and select Settings.
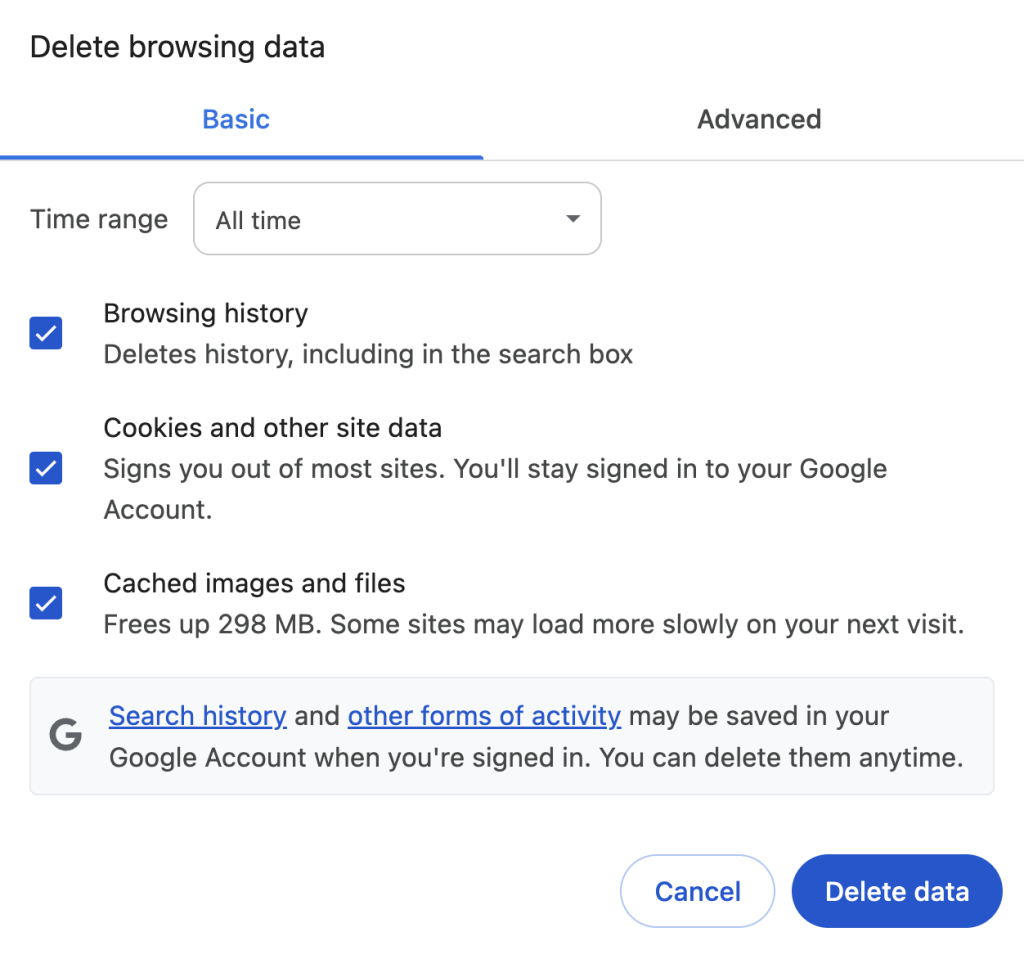
- Go to Privacy and security → Clear browsing data.
- Select the Basic tab and choose a time frame, such as All time.
- Check Browsing history, Cookies and other site data, and Cached images and files, then click Clear data.
- For a more thorough cleanup, choose the Advanced tab and select all available options.
Microsoft Edge
- Click the three horizontal dots icon and go to Settings → Privacy, search, and services.
- In the Clear browsing data now section, click Choose What to Clear.
- Under Time range, select your preferred time frame.
- Check each data type you wish to delete, such as Browsing history, Download history, Cookies and other site data, Cached images and files.
- Click Clear now.
Mozilla Firefox
- Click the hamburger menu and go to History → Clear recent history.
- Select a time frame from the dropdown menu.
- Check all available options and click Clear now. This will delete all browsing data, including the SSL state.
Safari
- Go to Safari → Settings from the top menu.
- Select the Privacy tab and click Manage Website Data.
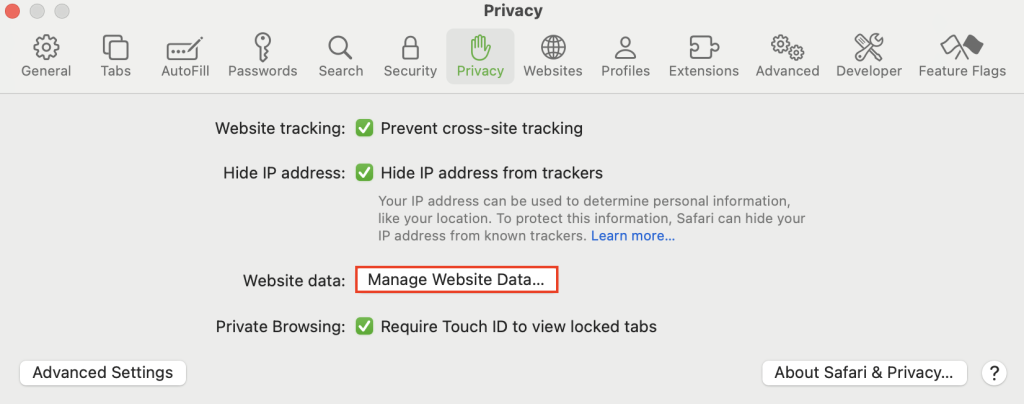
- Click Remove All and confirm your action.
Like Firefox, Safari clears the SSL state automatically when browsing data is erased.
If you use Windows, follow these additional steps to delete the SSL state:
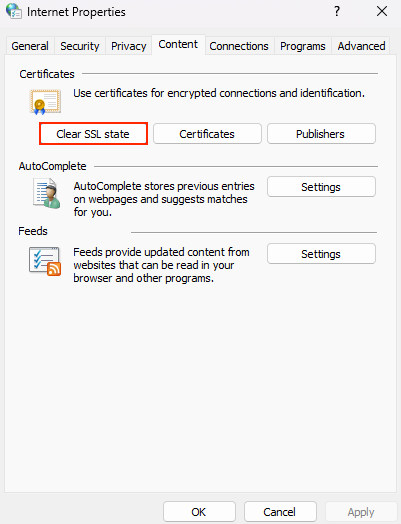
- Go to Control Panel → Network and Sharing Center → Internet Properties.
- Under the Content tab, click Clear SSL state.
Update the web browser and operating system
If you’ve set the correct date and time settings and cleared browser data but still face the ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR problem, try updating your browser and operating system.
Outdated software may lack the necessary updates to handle new security standards, causing SSL errors. Regular updates ensure that your browser and OS have the latest security patches, bug fixes, and features, reducing the risk of encountering these issues.
Users who install browsers from trusted sources like Android’s Play Store or the macOS and iOS App Store should check the marketplace for available updates and install them as needed.
However, if you downloaded the browser from the official site, you may need to update it manually. Here are the instructions:
Google Chrome
- Go to Settings → About Chrome.
- Chrome will automatically check for updates and install them if available.
- Click Relaunch to complete the update process.
Microsoft Edge
- Head to Help and feedback → About Microsoft Edge.
- Like Chrome, Edge will automatically check for updates and install them.
- Once done, restart the browser if needed.
Mozilla Firefox
Firefox automatically downloads and installs updates by default. If you have turned off this feature or want to ensure you have the latest version, follow these steps:
- Navigate to Settings and scroll down to the Firefox Updates section.
- Click Check for updates to see if there’s a new update available.
Meanwhile, here’s the guide to update your device’s OS:
Windows
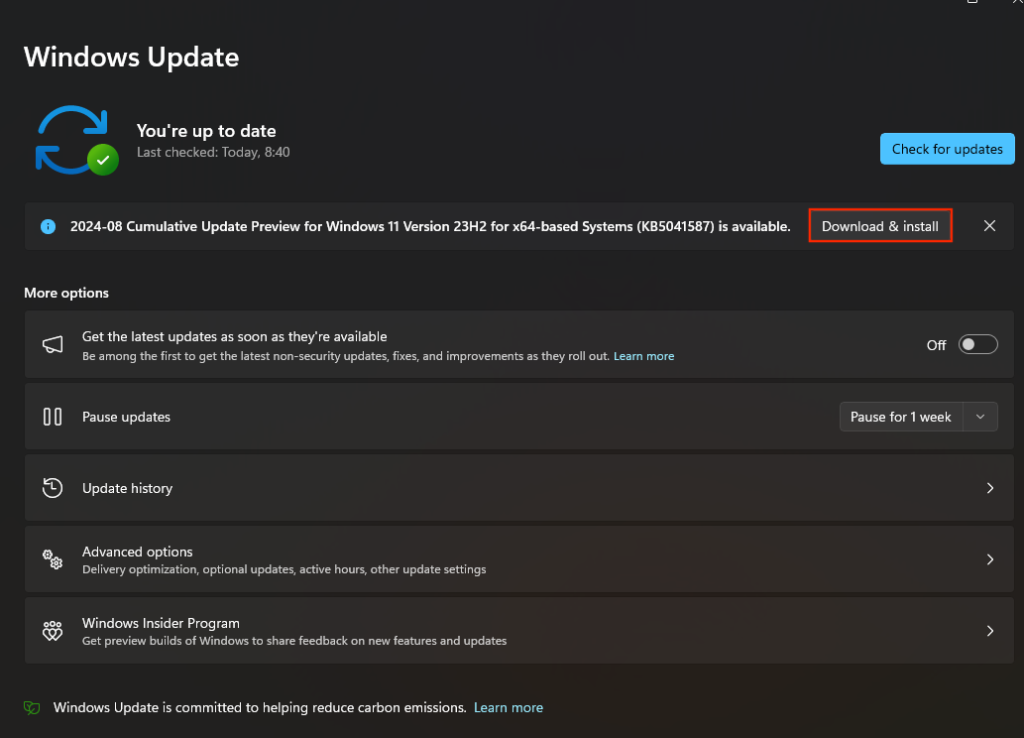
- Go to Settings → Windows Update.
- Click Check for updates.
- If updates are available, click Download & install.
macOS and iOS
- Navigate to System Settings or Settings → General → Software Update.
- Wait for the system to check for updates.
- If updates are available, click Update Now or Upgrade Now for a new version.
Android
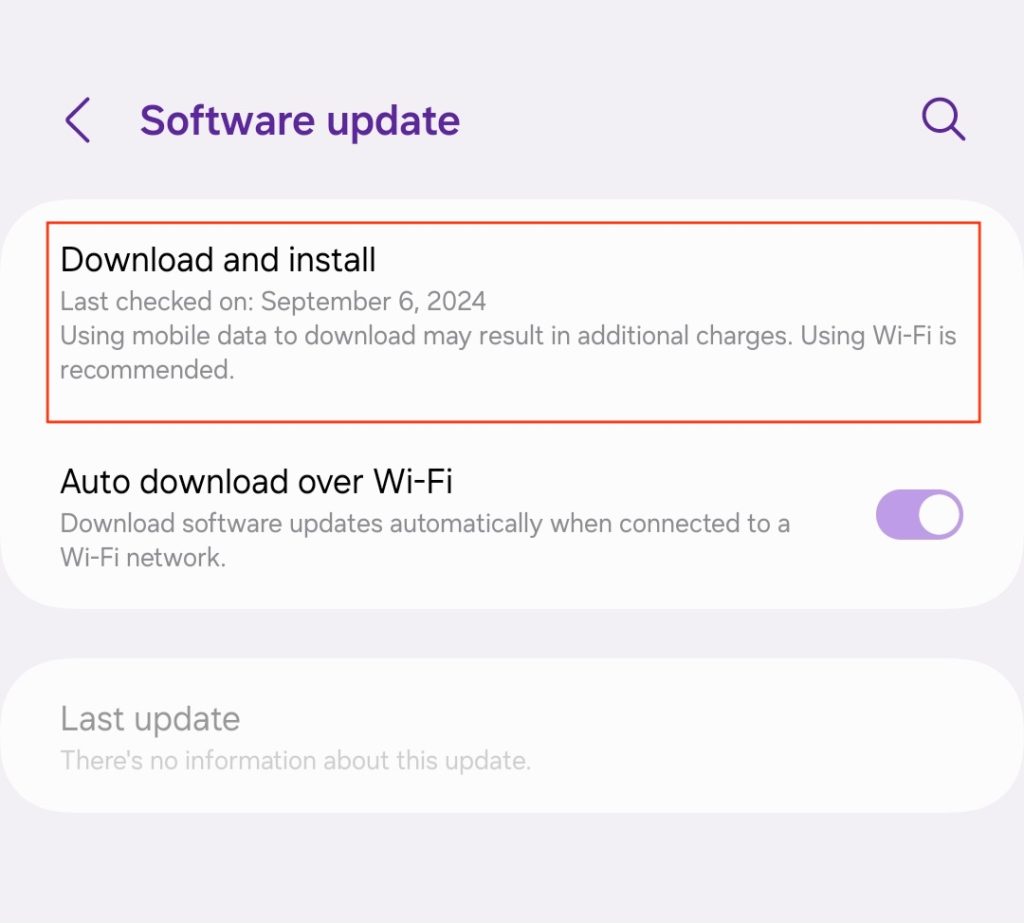
- Head to Settings → Software update.
- Tap Download and install. The device will automatically check for updates.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to install the update.
Disable conflicting extensions
Browser extensions, especially those related to security, privacy, or content filtering, can sometimes interfere with SSL connections, causing errors like ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR.
This happens because they may block certain elements or scripts necessary for a secure SSL handshake. Disabling conflicting extensions can help troubleshoot and fix these issues by identifying the problem’s source. Follow these steps:
Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge
- Click the Extensions icon in the toolbar and select Manage Extensions.
- Review the list of installed extensions and toggle off any that might be causing conflicts, such as ad-blockers or security add-ons.
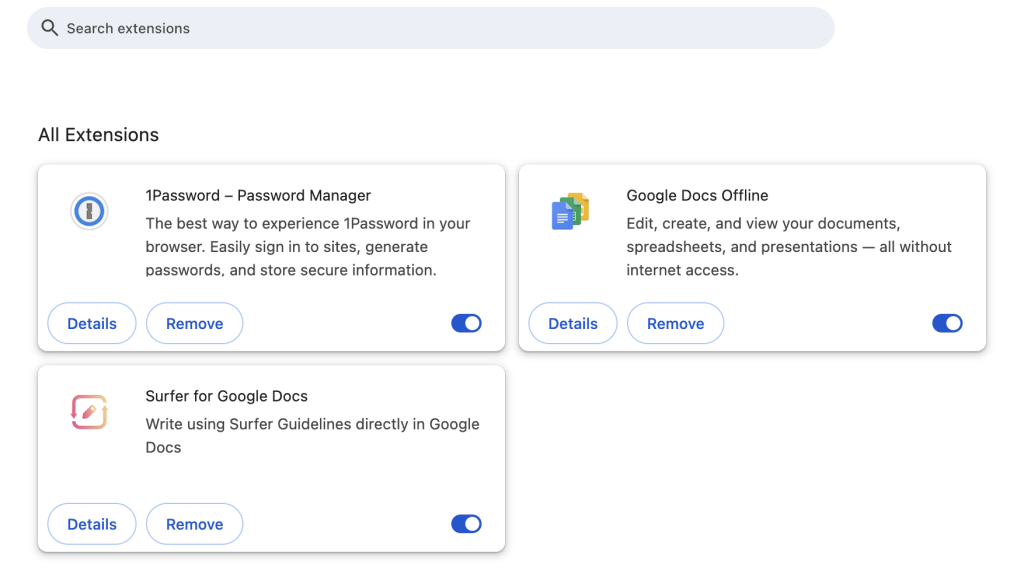
- Refresh the page to see if the error persists. If it does, try turning off more extensions one by one.
- Otherwise, turn it off one by one to identify the culprit.
- Click Remove under the problematic extension to uninstall it completely.
Mozilla Firefox
- Go to Add-ons → Extensions from the hamburger menu.
- Disable extensions by toggling the switch next to each one. Focus on privacy, security, and ad-blocker extensions first.
- Refresh the page to check if the error is resolved. Remove any unnecessary extensions by clicking Remove.
Safari
- Navigate to Safari → Settings → Extensions.
- Uncheck the box next to any extensions that might be causing the issue.
- Restart Safari and try reaccessing the website.
Use a VPN
A virtual private network (VPN) can sometimes resolve ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR if it’s caused by network restrictions, geo-blocks, or regional internet regulations.
A VPN masks your IP address and encrypts your internet traffic, so you can bypass these restrictions and access the website normally. Here are the instructions to set up a VPN:
- Select a reputable VPN service, then purchase a subscription plan or opt for a free version. For this example, we use NordVPN.
- Visit NordVPN’s official website and download the application that is compatible with your OS. Then, follow the provided installation instructions.
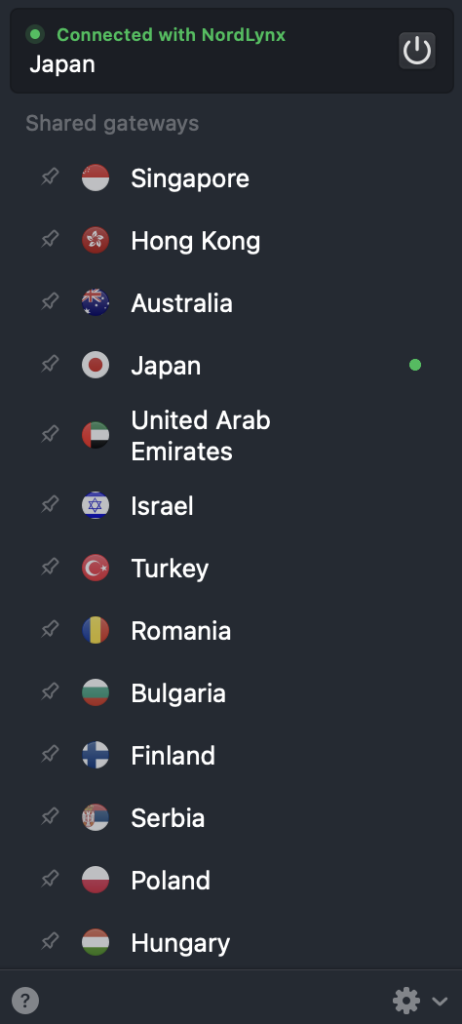
- Open the VPN service and log in with your credentials, or create a new account if you haven’t already.
- Select a gateway in a different region or country to bypass local network restrictions.
- Try opening the website again to see if the error no longer appears.
Disable antivirus and firewall temporarily
Antivirus and firewall settings protect your system by monitoring and blocking potentially harmful traffic. However, sometimes, these settings can prevent legitimate connections, leading to SSL protocol errors.
Temporarily disabling these programs can help determine if they cause the problem. Here’s how:
Windows Security
- Go to Settings → Privacy & Security → Windows Security.
- Click Virus & threat protection → Manage settings.
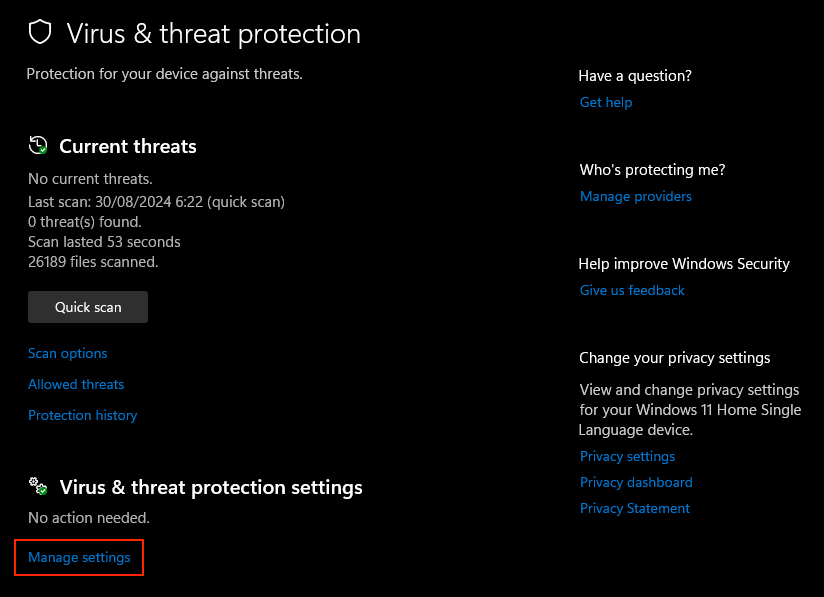
- Toggle Real-time protection to Off and click Yes to confirm.
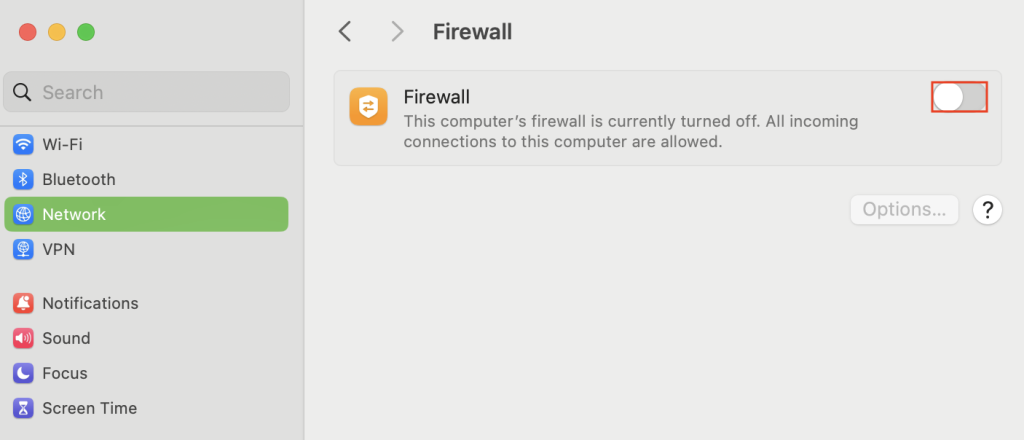
macOS Firewall
- Navigate to System Settings → Network → Firewall.
- Turn off the Firewall option.
Third-party antivirus program
If you use third-party antivirus software, look for an option to temporarily turn off real-time protection, web shield, or firewall. This option may be labeled differently, such as “Pause Protection,” “Turn Off,” or “Disable.”
After deactivating these security programs, try opening the same website to see if ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR persists.
Remember that permanently disabling antivirus or firewall software is not recommended. Instead, try configuring the settings to allow legitimate traffic, or consult the software’s support team if you’re unsure how to proceed.
Adjust SSL/TLS settings in the browser
Adjusting SSL/TLS settings in your browser can help resolve ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR if the error is caused by compatibility issues between the browser and the server’s SSL/TLS configurations.
Here are the instructions to adjust these settings in different browsers:
Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge
These Chromium-based browsers don’t provide direct settings for SSL/TLS protocols, but you can manage flags to enable or disable certain security features:
- In the address bar, type chrome://flags/ for Chrome or edge://flags/ for Edge and press Enter.
- Look for flags related to SSL/TLS and adjust them as needed.
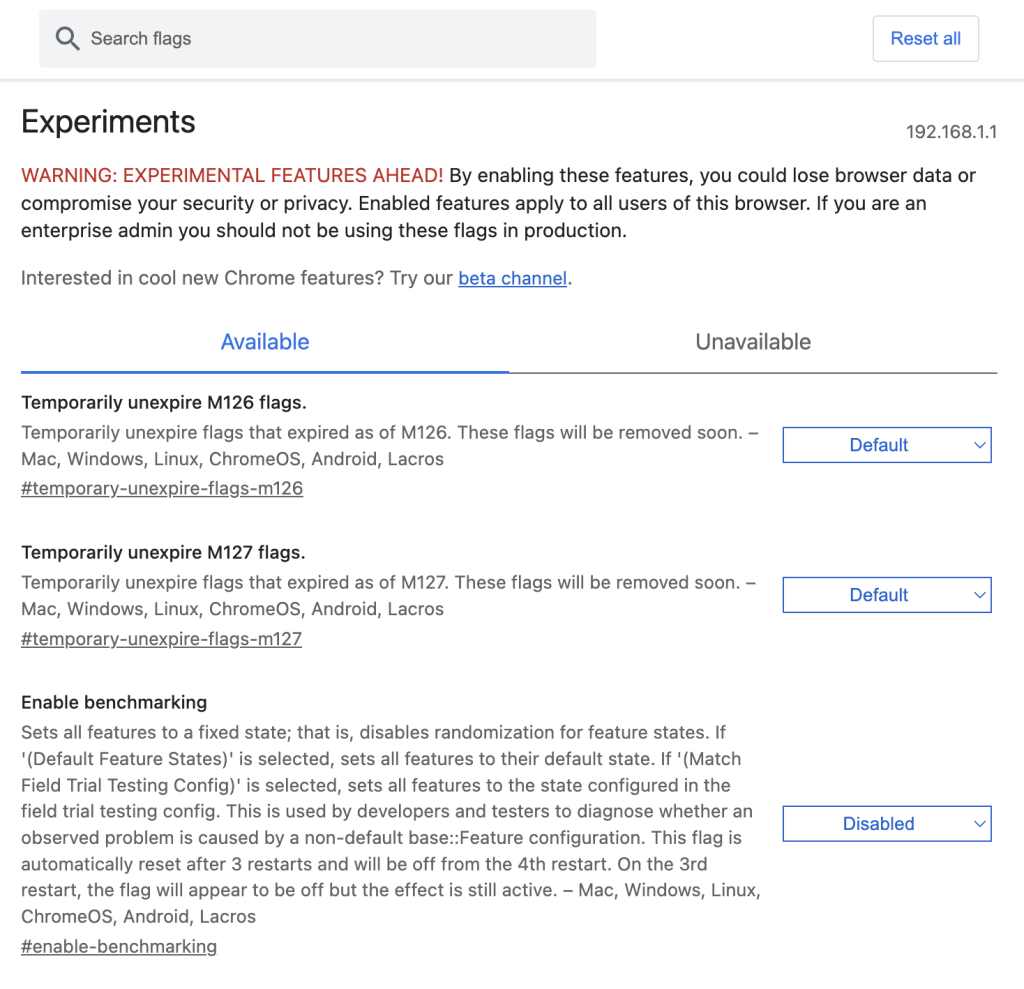
- Restart the browser to ensure the changes take effect.
Mozilla Firefox
Unlike Edge and Chrome, Firefox lets you adjust SSL/TLS settings through its configuration settings:
- Type about:config in the address bar and press Enter.
- Accept the warning and proceed.
- Set security.tls.version.min to 3 to enable TLS 1.2 as the minimum version and set security.tls.version.max to 4 to enable TLS 1.3 as the maximum version.
- Restart Firefox to apply the changes.
Similar to disabling antivirus and firewall, this method should only be used as a temporary solution. Lowering browser security settings can expose you to risks, such as allowing outdated encryption protocols or vulnerable connections.
Reset network settings
Network settings control how your device connects to the internet, including DNS configurations, IP and proxy settings, and firewall rules. Over time, these settings can become corrupted or misconfigured due to software updates, network changes, or conflicting settings.
Resetting them to their default state can help eliminate SSL-related issues like ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR and restore a secure connection. Here’s how:
Windows
- Open the Terminal or Command Prompt application with administrative privileges.
- Enter the following commands one by one, pressing Enter after each:
netsh int ip reset netsh winsock reset ipconfig /flushdns
- Restart your computer to apply the changes.
macOS
- Go to System Settings → Network.
- Select your active network connection, Wi-Fi or Ethernet, and click Details.
- Click Forget This Network and confirm the deletion.
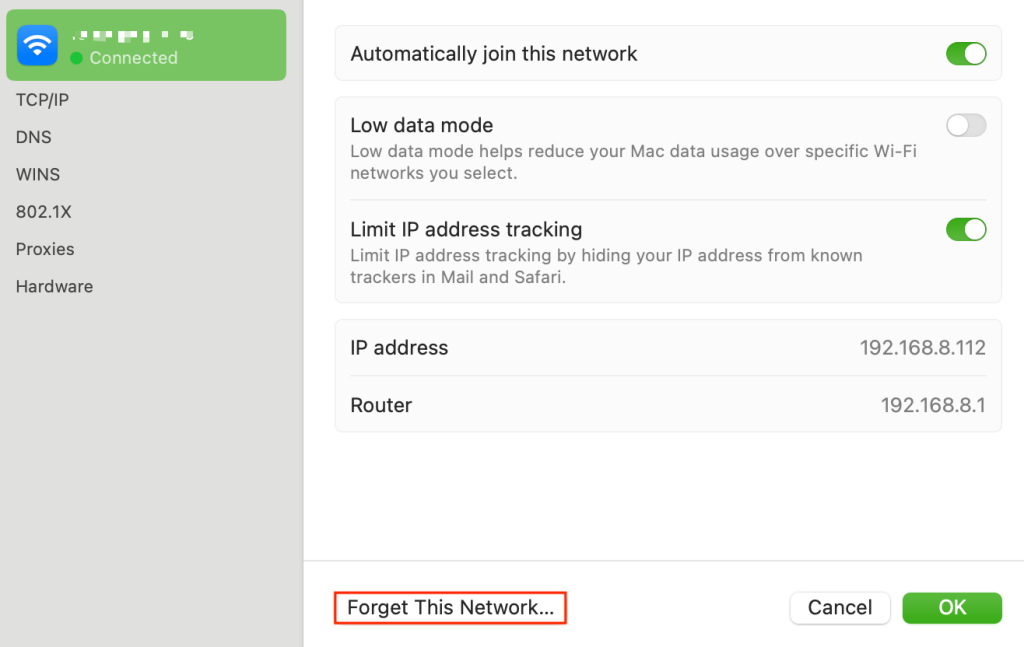
- Re-add your network connection and configure it as needed.
Android
- Open Settings and go to General management → Reset.
- Tap Reset network settings and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Repeat the same process in the Reset Wi-Fi and Bluetooth settings menu.
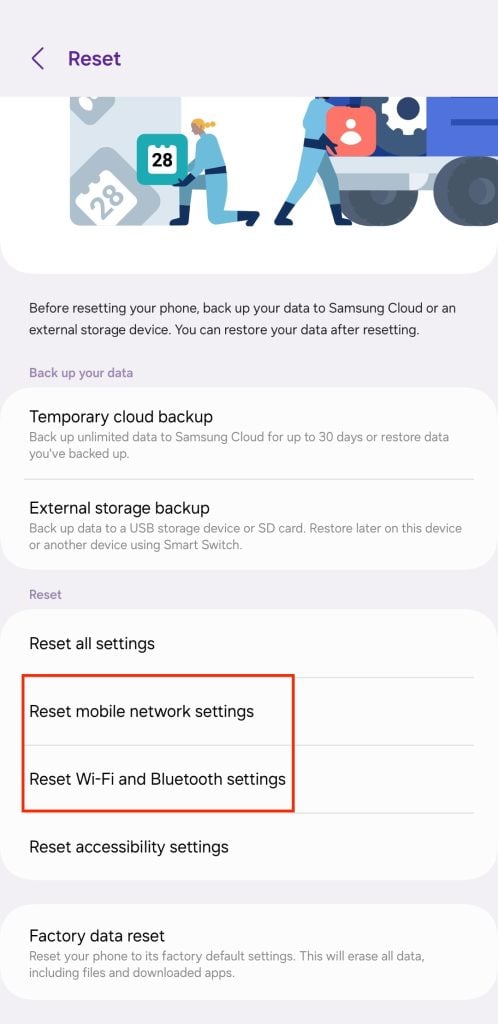
- Your network settings will be reset to default, and you’ll need to reconnect to your Wi-Fi network.
iPhone
- Go to Settings → General → Reset.
- Tap Reset Network Settings.
- Enter your passcode if prompted and confirm the reset.
- Your device will restart, and network settings will be restored to default.
Pro Tip
Encountering an ERR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCH error? Discover the step-by-step guide to fix it in our detailed article.
The subsequent methods are intended for website owners to troubleshoot server-side configurations and SSL certificate issues.
Check for mixed content issues
Mixed content happens when a web page loads insecure HTTP elements, such as images, scripts, or stylesheets, over a secure HTTPS connection. This causes browsers to block access or display a warning, negatively affecting user trust and site security.
Here’s how to identify and resolve mixed content issues for website owners:
- Use browser developer tools to inspect the console for mixed content warnings: For Google Chrome, right-click anywhere on the page and select Inspect → Console. Look for “Mixed Content” warnings that indicate which resources are being loaded over HTTP.
- Update all internal resource URLs to use HTTPS instead of HTTP. This might involve editing the HTML, CSS, or JavaScript files directly or using a plugin for CMS platforms like WordPress. Ensure that third-party resources are also loaded over HTTPS.
- Use server-side redirects like 301 to force all HTTP traffic to HTTPS. For example, in an .htaccess file for an Apache server, you can add:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} off
RewriteRule (.*) https://%{HTTP_HOST}%{REQUEST_URI} [L,R=301]
For NGINX servers, add a redirect rule in the server block:
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com www.example.com;
return 301 https://example.com$request_uri;
}
- After updating links and setting up redirects, clear your browser cache and refresh the page to see if the error is resolved.
Check SSL/TLS certificate validity
SSL/TLS certificates help encrypt data transmitted between the user and server, ensuring privacy and protection from potential threats. If an SSL/TLS certificate is expired, improperly configured, or revoked, it can trigger problems like ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR.
Therefore, you must regularly verify your SSL/TLS certificate’s validity to maintain a secure and trustworthy website. Follow these steps:
- Use online tools like Qualys SSL Labs or Why No Padlock? to check your website’s SSL/TLS certificate status. These tools help you identify issues like expired certificates, weak ciphers, or mismatched domain names.
- Enter your website URL into these tools, and they will run a comprehensive check and highlight any problems with the certificate.
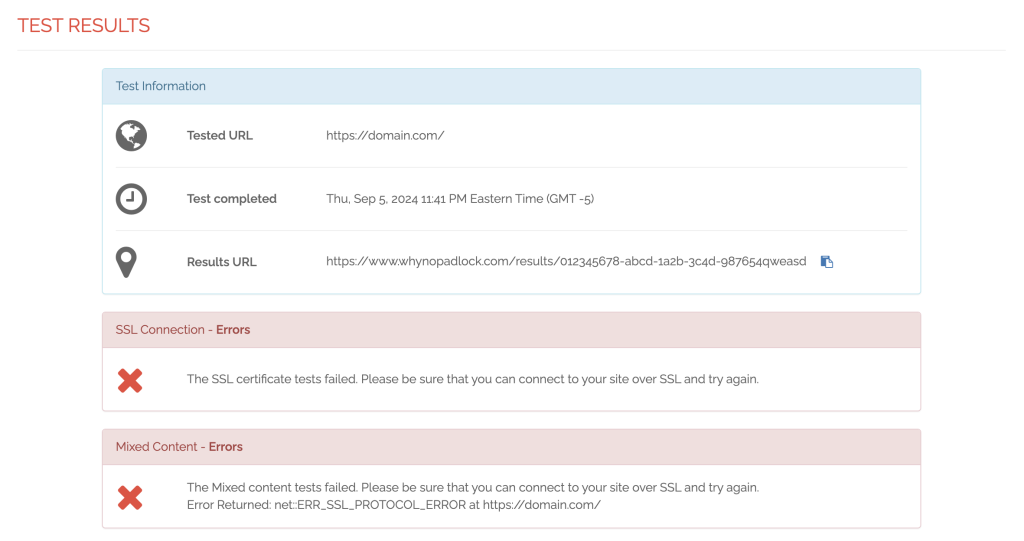
If it turns out that your SSL/TLS certificate has expired or is misconfigured, you need to renew or reissue it. The process depends on how you obtained your SSL certificate, but here are the general steps:
- Log in to your SSL certificate provider’s account.
- Locate the section for managing SSL certificates and select the expired one.
- Choose the option to renew or reconfigure the certificate. Follow the on-screen instructions to generate a new private key and certificate signing request (CSR) if required.
- Complete the domain validation process as instructed by your SSL provider.
- If available, activate the auto-renew feature so you don’t have to renew your SSL certificate manually every time it expires.
Verify server configuration
Misconfigured server settings, such as incorrect SSL certificate installation or outdated protocols, can lead to broken connections and errors like ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR.
Follow these basic guidelines to ensure your server is correctly configured:
- Verify that the SSL certificate, intermediate certificates, and private key are correctly installed on the server. A missing intermediate certificate can cause the SSL handshake to fail. Use the SSL Certificate Checker to verify that your SSL chain is complete.
- Ensure your server is configured to support the latest and most secure versions of SSL/TLS protocols. Outdated protocols like SSL 2.0 and SSL 3.0 should be disabled, while TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3 should be enabled.
If you use an Apache web server, update your configuration file to include the SSLProtocol directive:
SSLProtocol all -SSLv2 -SSLv3
For NGINX servers, update ssl_protocols in the configuration file:
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
- Use strong cipher suites that provide solid encryption for your server. Weak cipher suites can also lead to SSL issues. You can use Mozilla’s SSL Configuration Generator to generate secure cipher suite configurations for Apache, NGINX, and other web servers.
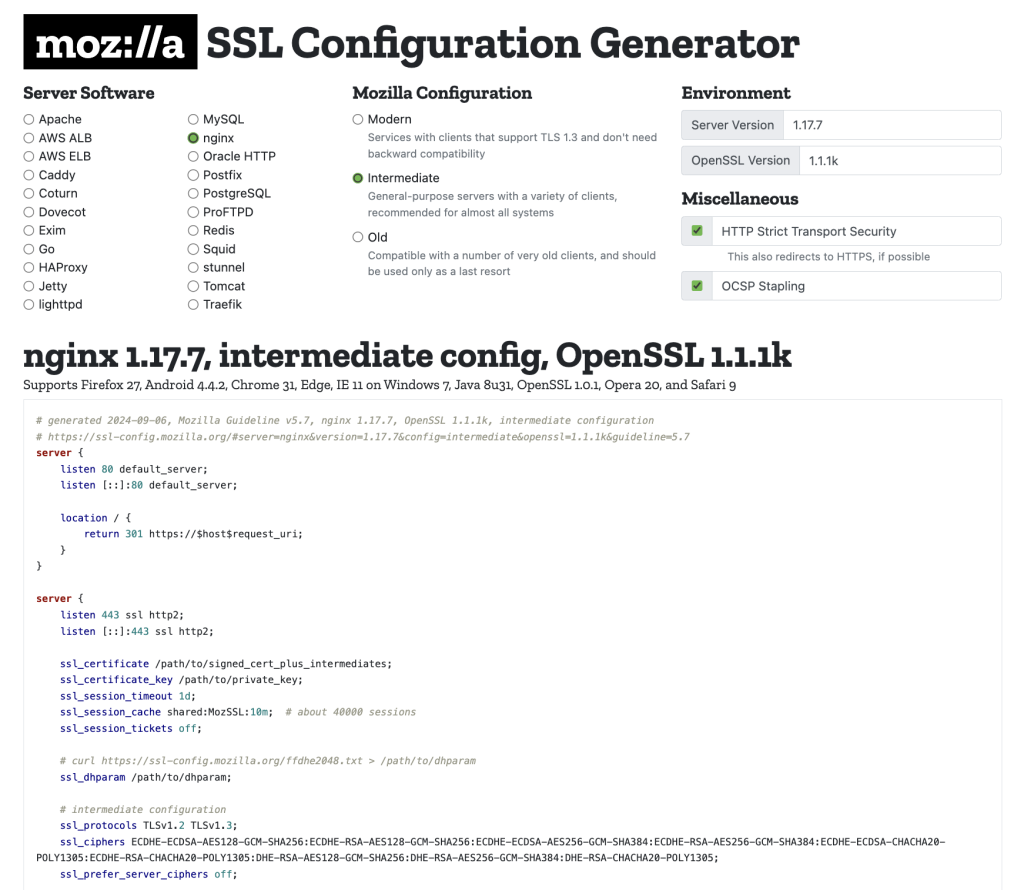
- After changing your server configuration, restart the web server to apply the updates. For Apache, use this command:
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Meanwhile, for NGINX, run the following instead:
sudo systemctl restart nginx
- Use the same SSL Certificate Checker tool again to check for any remaining warnings or errors and address them accordingly.
Preventing ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR in the future
Here are some strategies you can implement to prevent ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR from recurring on your website:
Regularly update certificates
Keeping SSL certificates up to date is essential for ensuring a secure connection. Monitor your certificates’ expiration dates continuously and set up auto-renewal if available.
If auto-renewal is not an option, schedule reminders to renew your certificates in advance. Regularly check that the certificate chain is complete and correctly installed to avoid unexpected issues.
Implement SSL best practices
Applying essential SSL/TLS best practices can help maintain a secure web environment. Use strong cipher suites, ensure your server only supports TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3, and deactivate outdated protocols like SSL 2.0 and SSL 3.0.
Enforce HTTPS across your entire website by implementing 301 redirects from HTTP to HTTPS and using the HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) header to prevent users from accessing insecure versions of your site.
Conduct regular maintenance
Regular server and website maintenance is necessary to prevent errors. This includes updating server software, plugins, and frameworks to their latest versions, checking server configurations, and performing security audits.
Periodic maintenance helps ensure that your SSL/TLS settings remain secure and up to date, reducing the risk of SSL-related errors.
Set up monitoring and alerts
Use SSL monitoring tools such as Qualys SSL Labs, Why No Padlock?, or SSL Certificate Checker to detect issues early and receive alerts for expired or misconfigured certificates.
These tools can automatically check your SSL certificates’ health and notify you of any problems. This proactive approach helps address potential issues before they impact users and ensures your website remains secure and accessible.

Conclusion
ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR can disrupt secure access to websites and negatively impact user experience. This article has covered several ways to identify and fix the issue, such as checking date and time settings, using a VPN, and verifying SSL/TLS certificate validity.
To prevent this issue from recurring in the future, website owners should regularly update certificates, implement SSL best practices, conduct server and website maintenance, and set up monitoring tools.
If you still have questions about ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR or want to share additional tips to resolve this problem, please use the comment box below.
ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR FAQ
Why am I seeing the ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR message?
The ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR message often appears due to expired or misconfigured SSL certificates, incorrect date and time settings, outdated browser or OS, mixed content issues, or antivirus or firewall software interference.
How can I fix the ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR?
To fix ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR, check the SSL/TLS certificate’s validity, clean browsing data, disable browser extensions, ensure firewall and antivirus settings allow secure connections, and reset network configurations.
Are there specific web browsers that are more prone to showing this error message?
Modern web browsers like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, and Microsoft Edge are more sensitive to SSL errors because they strictly enforce SSL/TLS protocols and security standards to ensure user safety and data protection.